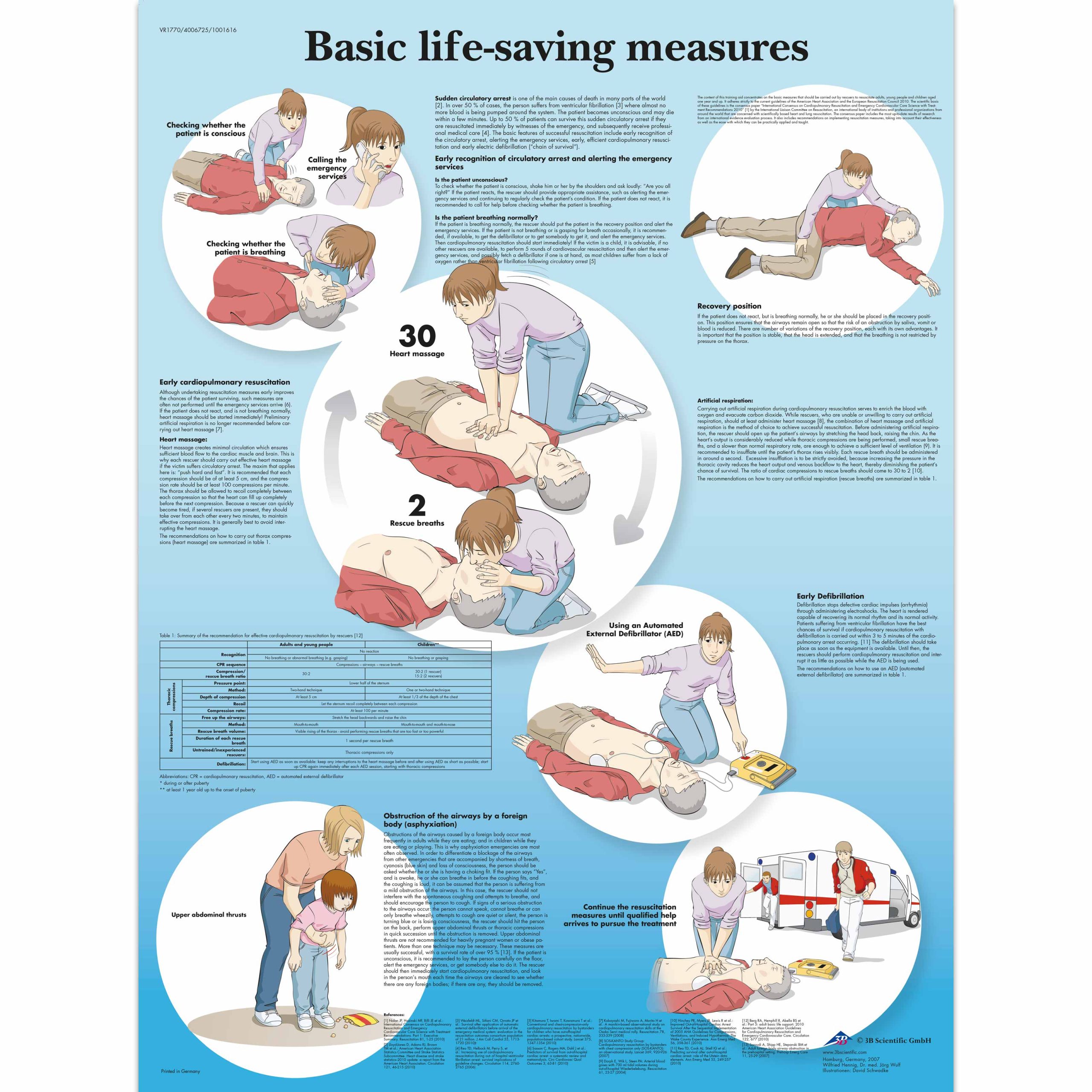
Basic Life Support (BLS) is a critical skill that provides emergency care for individuals experiencing cardiac arrest or other life-threatening situations. Learn the essentials to save lives!
Basic Life Support (BLS), a fundamental aspect of emergency medical care, is a critical skill that can mean the difference between life and death in a medical emergency. Whether you are a healthcare professional or a concerned bystander, having a strong foundation in BLS techniques is essential for providing immediate assistance to someone experiencing cardiac arrest or other life-threatening conditions. With its emphasis on prompt action and effective interventions, BLS equips individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to stabilize a patient until advanced medical help arrives. In this paragraph, we will explore the key components of BLS, highlighting the importance of understanding and applying these techniques in emergency situations.
Introduction
Basic Life Support (BLS) is a critical set of skills and techniques that are used to sustain life in emergency situations. It is the immediate care provided to individuals who are experiencing cardiac arrest, respiratory distress, or any other life-threatening condition. BLS aims to maintain the vital functions of the body until advanced medical care can be given.
The Importance of Basic Life Support
Basic Life Support plays a crucial role in saving lives during emergencies. Immediate response and effective application of BLS techniques can significantly increase the chances of survival for individuals in critical conditions. This type of support can be provided by healthcare professionals, bystanders, and even family members who have received proper training.
Key Components of Basic Life Support
Basic Life Support comprises several essential components, including:
CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation)
CPR involves performing chest compressions and rescue breaths to manually circulate blood and oxygen to the body’s vital organs when the heart has stopped beating or is not effectively pumping blood.
Airway Management
Airway management ensures that the patient’s airway is open and clear to facilitate breathing. This may involve techniques such as head tilt-chin lift or jaw thrust maneuvers.
Use of Automated External Defibrillator (AED)
An AED is a portable device that delivers an electric shock to the heart in cases of cardiac arrest. BLS training often includes instruction on how to properly use an AED.
Who Should Learn Basic Life Support?
Basic Life Support training is highly recommended for anyone, regardless of their profession or background. However, certain individuals can benefit greatly from learning BLS:
Healthcare Professionals
Doctors, nurses, paramedics, and other healthcare providers are required to have BLS certification. They often encounter critical situations where immediate intervention is crucial.
Teachers and School Staff
Being trained in BLS can be invaluable for educators and school staff who work with children. They may need to respond to emergencies that occur within the school premises.
Parents and Caregivers
Parents and caregivers should consider learning BLS to ensure they can provide immediate assistance to their loved ones during emergencies.
How to Perform Basic Life Support
Performing Basic Life Support requires proper training and knowledge. Here’s a general overview of the steps involved:
1. Assess the Situation
Before providing BLS, ensure that the scene is safe for both you and the victim. Identify any potential hazards or risks.
2. Check Responsiveness
Tap the victim and shout to determine if they are responsive. If there is no response, proceed to the next steps.
3. Call for Help
Contact emergency services or ask someone nearby to call for help. Time is critical in these situations.
4. Perform CPR
Start chest compressions by placing the heel of one hand on the center of the victim’s chest. Interlock your other hand and deliver compressions at a rate of 100-120 per minute.
5. Use an AED (if available)
If an AED is accessible, follow the device’s instructions to provide a shock if necessary.
6. Continue CPR
Alternate between chest compressions and rescue breaths until medical professionals take over or the victim shows signs of life.
BLS Certification
Obtaining BLS certification involves completing a training course that covers the necessary skills and knowledge. These courses are offered by various organizations, including the American Heart Association and the Red Cross. Certification is typically valid for a certain period, after which individuals need to undergo re-certification to ensure their skills are up to date.
Conclusion
Basic Life Support is an essential set of skills that can make a significant difference in emergency situations. By learning BLS techniques, anyone can become equipped to provide immediate care and increase the chances of survival for those in need. Whether you’re a healthcare professional or a concerned citizen, investing time in BLS training is a valuable step towards saving lives.
Introduction: Understanding the Importance of Basic Life Support
Basic Life Support (BLS) is a crucial set of skills and techniques that can mean the difference between life and death in emergency situations. It is the immediate care provided to individuals experiencing life-threatening emergencies, such as cardiac arrest, choking, or severe bleeding. BLS aims to stabilize the patient’s condition until advanced medical help arrives. Whether you are a healthcare professional or a layperson, having knowledge of BLS is essential as it empowers you to respond effectively during emergencies and potentially save lives.
Significance of Early Recognition: Identifying Life-Threatening Emergencies
Early recognition is the first step in providing effective basic life support. Being able to quickly identify life-threatening emergencies allows for prompt action and increases the chances of a positive outcome. By recognizing symptoms such as unconsciousness, absence of breathing, or severe bleeding, individuals can activate the emergency medical system and initiate basic life support measures. Early recognition ensures that appropriate medical assistance is summoned promptly, which is critical in saving lives.
Essential Steps in Basic Life Support: The ABCs (Airway, Breathing, Circulation)
The foundation of basic life support lies in the ABCs – Airway, Breathing, and Circulation. These steps must be followed in sequential order to provide effective care. First, ensure that the victim’s airway is clear by placing them on their back and opening their airway using the head-tilt, chin-lift maneuver. Next, assess for breathing by looking, listening, and feeling for any signs of breathing. If the victim is not breathing, provide rescue breaths by giving two breaths while watching for chest rise. Lastly, check for circulation by feeling for a pulse at the carotid artery in the neck. If no pulse is present, begin chest compressions immediately.
Performing CPR: Providing Chest Compressions and Rescue Breaths
CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) is a critical component of basic life support. It involves the combination of chest compressions and rescue breaths to maintain blood flow and oxygenation to vital organs. To perform CPR, position yourself next to the victim and place the heel of one hand on the center of their chest. Interlock your other hand on top and align your shoulders directly above your hands. With straight arms, apply firm and rhythmic compressions at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute. After every 30 compressions, deliver two rescue breaths by sealing your mouth over the victim’s mouth and nose and providing a full breath. Continue CPR until advanced medical help arrives or the victim shows signs of recovery.
Familiarizing with AED: Using an Automated External Defibrillator for Cardiac Arrest
In cases of cardiac arrest, an Automated External Defibrillator (AED) plays a vital role in basic life support. AEDs are portable devices that can analyze the heart rhythm and deliver an electric shock if necessary. When using an AED, follow these steps: 1) Power on the device and attach the electrode pads to the victim’s bare chest as instructed; 2) Allow the AED to analyze the heart rhythm and follow its prompts; 3) If a shock is advised, ensure no one is in contact with the victim and press the shock button; 4) Immediately resume CPR after the shock is delivered. AEDs are designed to be user-friendly and can greatly increase the chances of restoring a normal heart rhythm in cardiac arrest cases.
Recognizing Choking: Administering Effective Maneuvers to Clear Airway
Choking is a life-threatening emergency that requires immediate action. When someone is choking, their airway is partially or completely blocked, preventing them from breathing adequately. To assist a choking victim, follow these steps: 1) Encourage the victim to cough forcefully to try and dislodge the object; 2) If coughing doesn’t work, stand behind the victim and deliver five back blows between the shoulder blades using the heel of your hand; 3) If the obstruction persists, perform five abdominal thrusts by standing behind the victim, placing your hands above their navel, and delivering inward and upward thrusts. Continue alternating between back blows and abdominal thrusts until the obstruction is cleared or emergency medical help arrives.
Managing Bleeding: Applying Basic First Aid Techniques to Control Hemorrhage
Severe bleeding can be life-threatening if not addressed promptly. Basic life support includes knowing how to control bleeding effectively. To manage bleeding, follow these steps: 1) Put on disposable gloves to protect yourself from potential infection; 2) Apply direct pressure to the wound using a sterile dressing or clean cloth; 3) If the bleeding continues, apply additional dressings and maintain pressure; 4) Elevate the injured area above the level of the heart, if possible, to help reduce blood flow; 5) If bleeding cannot be controlled with direct pressure, consider applying a tourniquet as a last resort. Properly managing bleeding is crucial in preventing excessive blood loss and ensuring the victim’s stability until professional medical assistance is available.
Dealing with Shock: Understanding Signs and Providing Appropriate Care
Shock occurs when there is insufficient blood flow to meet the body’s oxygen and nutrient demands. It can be caused by various factors, such as severe bleeding, trauma, or medical conditions. Recognizing the signs of shock, including pale and cool skin, rapid breathing, weak pulse, and altered mental status, is crucial in providing appropriate care. When managing shock, ensure the victim is lying flat on their back with their legs elevated about 12 inches, if no spinal injury is suspected. Keep the victim warm and monitor their vital signs until medical help arrives. By addressing shock promptly and effectively, you can improve the chances of a positive outcome for the victim.
Handling Spinal Injuries: Ensuring Proper Immobilization and Preventing Further Damage
Spinal injuries require special attention during basic life support to prevent further damage. If a spinal injury is suspected, it is essential to keep the victim’s head, neck, and back in alignment and immobilize them until professional medical help arrives. Follow these steps to handle spinal injuries properly: 1) Support the victim’s head and neck in a neutral position using your hands until a cervical collar or other immobilization device is applied; 2) Keep the victim still and avoid any unnecessary movement; 3) If the victim needs to be moved, maintain alignment of the head, neck, and back by enlisting the help of others. By ensuring proper immobilization, you can minimize the risk of exacerbating spinal injuries and potential neurological damage.
Practicing Synchronous Communication: Coordinating Efforts with Healthcare Professionals for Timely Assistance
In emergency situations, effective communication between bystanders and healthcare professionals is vital for timely assistance. Practicing synchronous communication involves relaying accurate information, following instructions, and coordinating efforts seamlessly. When contacting emergency medical services, provide clear and concise details about the situation, location, and patient’s condition. Stay on the line until instructed otherwise and follow any guidance given by the healthcare professional. Working together with healthcare professionals ensures a smooth transition of care and maximizes the chances of a positive outcome for the victim.
Point of View: Basic Life Support (BLS) Use
When it comes to providing life-saving assistance in emergency situations, Basic Life Support (BLS) plays a crucial role. BLS techniques are designed to stabilize patients and maintain their vital functions until advanced medical help arrives. In this article, we will explore the importance of BLS and discuss its key components.
Voice: Informative
-
BLS is a critical set of skills that can be performed by trained individuals with no medical background.
-
It is important to note that BLS procedures should only be carried out by individuals who have received proper training and certification.
-
By providing clear and concise instructions on BLS techniques, we aim to equip readers with the necessary knowledge to potentially save lives.
Tone: Empowering
-
Understanding and implementing BLS procedures can empower individuals to take action during emergencies and make a meaningful difference in someone’s life.
-
Through learning BLS, one can gain the confidence and skills needed to react effectively in high-pressure situations.
-
By disseminating information about BLS, we hope to inspire individuals to take the necessary steps to become certified in these life-saving techniques.
Key Components of Basic Life Support:
-
CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation): This technique involves chest compressions and rescue breaths to maintain blood flow and oxygenation in a person experiencing cardiac arrest.
-
Airway Management: Opening and maintaining a clear airway is crucial to ensure proper breathing. Techniques such as head tilt-chin lift or jaw thrust are used to achieve this.
-
Use of Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs): AEDs deliver an electric shock to restore the heart’s normal rhythm in cases of sudden cardiac arrest. Knowing how to operate an AED can significantly increase the chances of survival.
-
Hemorrhage Control: Rapidly controlling severe bleeding through direct pressure, wound packing, or the use of tourniquets can prevent hypovolemic shock and improve patient outcomes.
-
Recognition and Response to Respiratory Arrest: Identifying signs of respiratory distress or failure and responding promptly with appropriate interventions like rescue breaths or bag-valve-mask ventilation can be life-saving.
By understanding the importance of BLS and familiarizing ourselves with its key components, we can be better prepared to handle emergency situations and potentially save lives. Remember, timely and effective BLS can make all the difference when every second counts.
Thank you for taking the time to visit our blog and learn about Basic Life Support (BLS). We hope that the information provided has been valuable in helping you understand the importance of BLS and how it can save lives in emergency situations. As you have read, BLS is a critical set of skills that anyone can learn, regardless of their background or profession.
By acquiring BLS knowledge and training, you are empowering yourself to be a first responder in emergency situations. Whether it’s performing CPR on someone experiencing cardiac arrest or assisting someone who is choking, your ability to provide immediate care can make a significant difference in the outcome for the victim. BLS techniques are simple yet effective, and they can truly be life-saving.
We encourage you to take the next step and get certified in BLS. There are various organizations and institutions that offer BLS courses, both online and in-person, which can equip you with the necessary skills and knowledge. Becoming certified in BLS not only enhances your personal capabilities but also provides peace of mind knowing that you are prepared to handle emergencies effectively.
In conclusion, Basic Life Support is a crucial skillset that everyone should strive to acquire. It empowers individuals to become the first line of defense in emergency situations, potentially saving lives. By getting certified in BLS, you are taking a proactive step towards ensuring the safety and well-being of those around you. Remember, emergencies can happen at any time and anywhere, so being prepared with BLS knowledge is essential. Together, let’s make a difference and create a safer community!
Thank you once again for visiting our blog and showing interest in Basic Life Support. We hope you found the information provided informative and helpful. If you have any further questions or would like more resources on BLS, please feel free to reach out. Stay safe, stay prepared!